July 21st, 2016 – The first half of 2016 was characterized by a decline in the Spanish electricity market prices, when compared to the same period of the last year. This decline in prices was mainly caused by the increase of electricity production with less expensive technologies such as hydroelectric, wind power and nuclear, as well as the general decline in prices of fossil fuels used in electricity generation.
Evolution of the most important variables of the Spanish market in the first half of 2016
According to data published by REE, the growth in electricity demand was nil in the first half of 2016 compared with the same period of 2015. Once the influence of the temperature and the working days effect are taken into account, the growth in demand was 0.1% in a year-on-year basis. In the first quarter of this year the demand decreased by 1.3% over the same quarter last year, mainly because the temperatures in January and February were higher than the same months last year. On the other hand, in the second quarter of 2016 the demand was 1.5% higher on a year-on-year basis correlated with lower temperatures in this quarter compared with the same quarter last year.
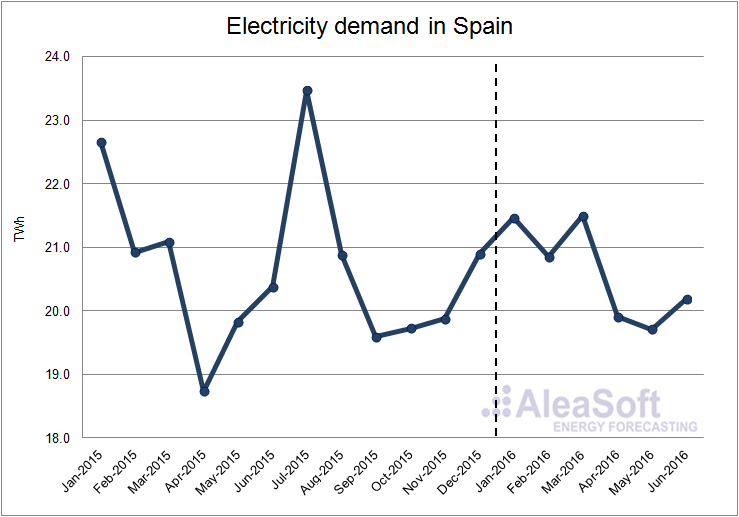
Evolution of electricity demand in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
The wind power production increased by 4.9% on a year-on-year basis. The production increase occurred mostly in the first quarter of this year, that was 8.6% higher than in the same quarter of last year, while in the second quarter, the production fell by 0.1% with respect to the second quarter of 2015, mainly because of a drop of 18.7% in May compared to May last year..
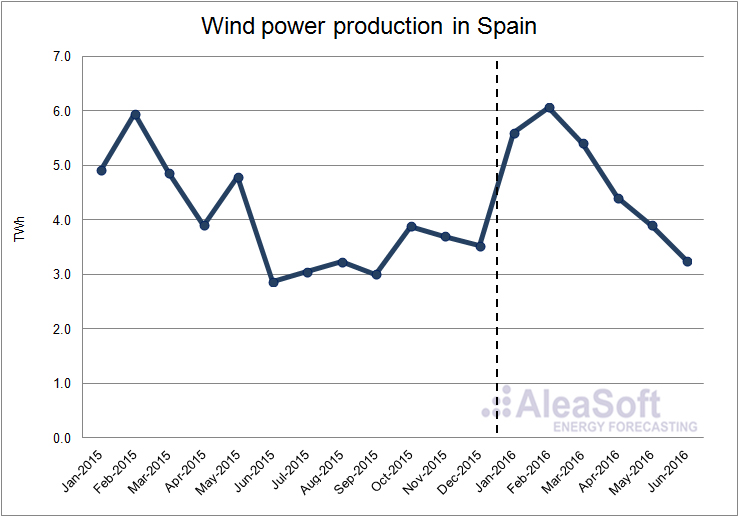
Evolution of wind production in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
The hydroelectric production increased considerably in the first half of 2016, raising 41.6% above the level of the first half of 2015. In the first six months of 2016 the hydroelectric production was higher month by month compared with the same month of last year, highlighting April where the production with this technology grew by 102.5% on a year-on-year basis.
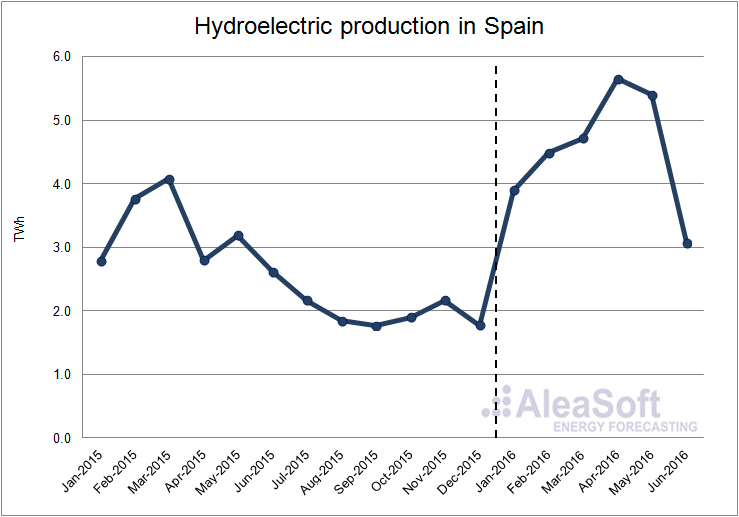
Evolution of hydroelectric production in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
The nuclear production increased by 1.4% in the first half of 2016 compared with the same period of the last year. The increase in the production was concentrated in the second quarter, where the production was 14.6% higher than in the second quarter of last year. On the contrary, in the first quarter of this year, the nuclear production was 9.2% lower than in the same quarter of last year.
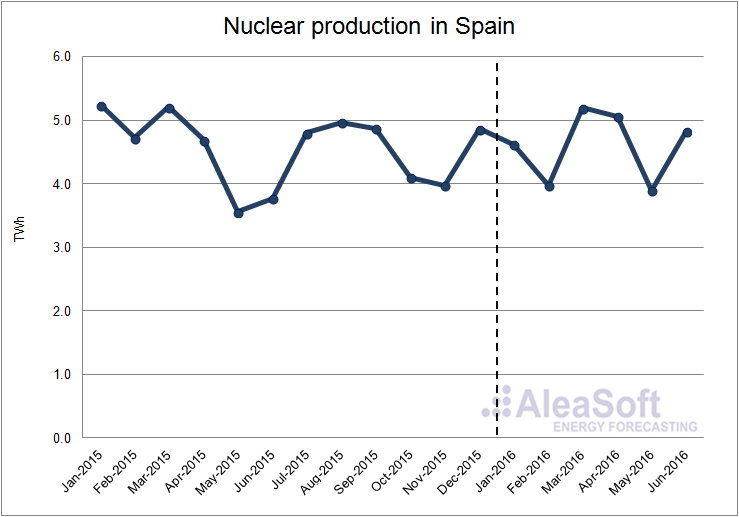
Evolution of nuclear production in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
The electricity generation using coal suffered a significant drop in the first half of 2016, where the production was 53.4% lower than in the first half of 2015. The production decreased on a year-on-year basis on each of the first six months of this year, mainly as a result of an increased hydroelectric production. According to data published by REE, in mainland Spain the installed power capacity of this technology until May 2016 decreased 932 MW in comparison with 2015.
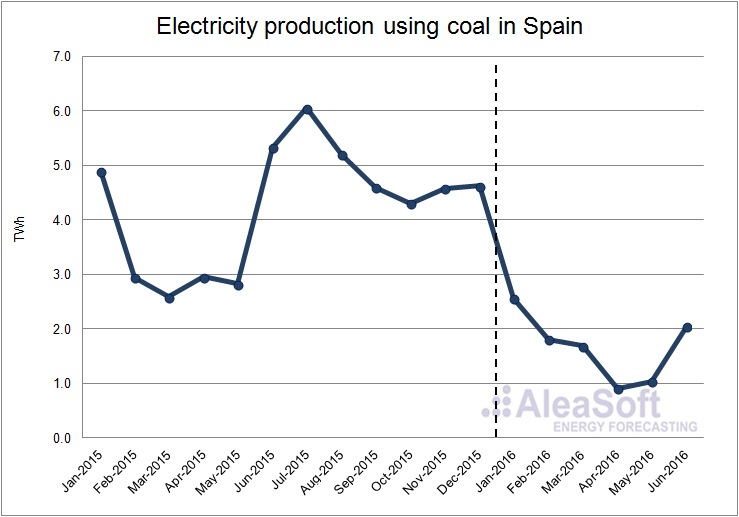
Evolution of electricity production using coal in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
The combined cycle production, like the coal but to a lesser extent, was affected by the increase of the hydroelectric production and diminished its production by 15.6% during the first half of 2016 compared with the same quarter of last year. According to data published by REE, in mainland Spain the installed power capacity of this technology until May this year did not change compared to 2015.
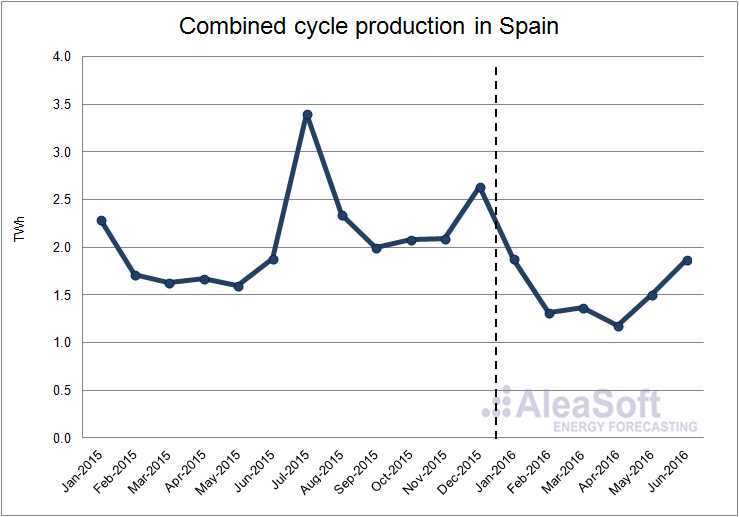
Evolution of combined cycle production in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
The photovoltaic production fell by 7.8% in the first half of this year compared to the same period of 2015. The decline on a year-on-year basis was of 11.1% in the first quarter and 5.6% in the second quarter.
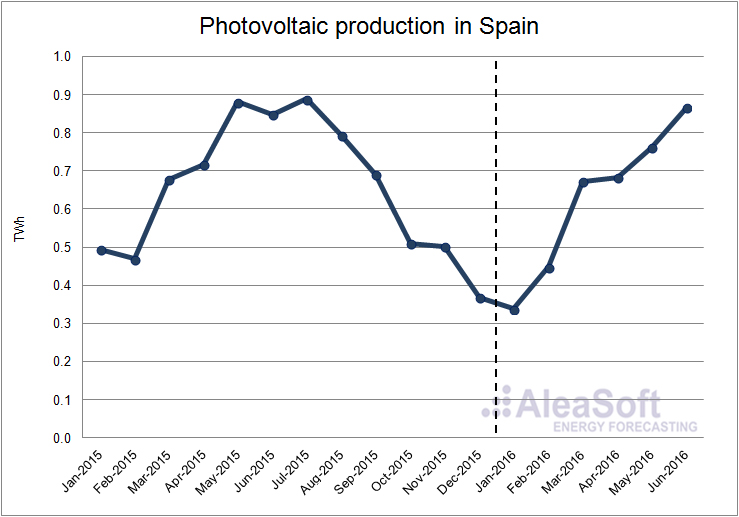
Evolution of solar photovoltaic production in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
In the case of solar thermal production, a fall of 10.5% was registered in the whole of the first six months of the year compared to the same period of 2015. The decrease was greater in the first quarter, where the production was 25.9% lower than in the same quarter of last year, while in the second quarter the production dropped by 3.8% on a year-on-year basis.
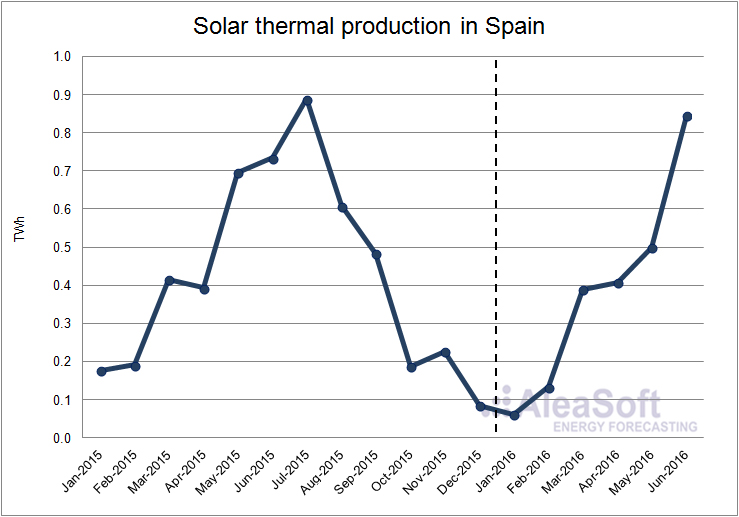
Evolution of solar thermal production in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
The production with other renewable technologies, that include biogas, biomass, marine energy and geothermal, decreased by 6.7% in the first half of 2016 compared with the first half of 2015. In this case the decline was greater in the second quarter, where production was 11.3% lower than in the same period of last year. In the first quarter of 2016 the production of these technologies fell by 2.3% compared with the first three months of 2015.
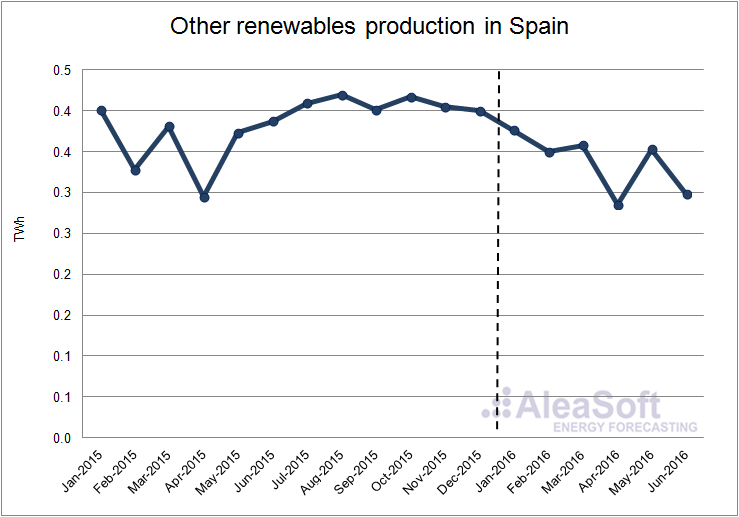
Evolution of production using other renewable technologies in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
The cogeneration production increased by 1.1% during the first half of 2016 compared to the same period of 2015. The production in the first two quarters of this year increased on a year-on-year basis: 0.3% in the first quarter and 1.9% in the second one.
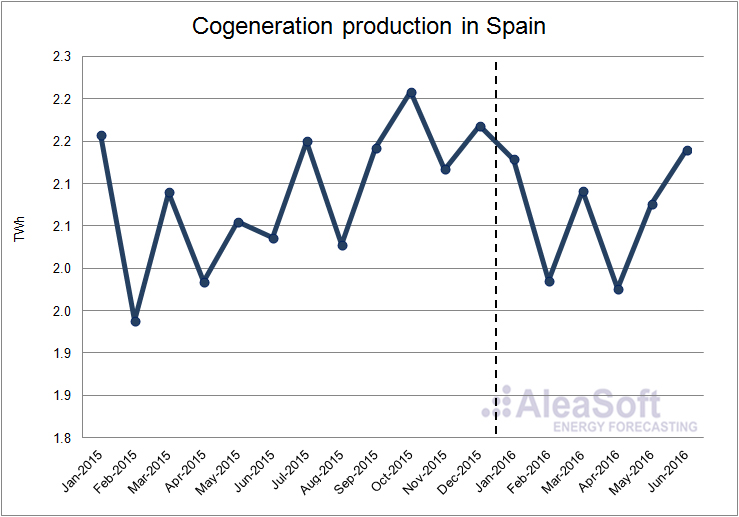
Evolution of cogeneration production in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
The electricity production using waste increased by 3.8% in the first half of this year over the same period of 2015. On a year-on-year basis, in the first quarter of 2016 the production increase using this technology was of 2.9%, while in the second, it was 4.5%.
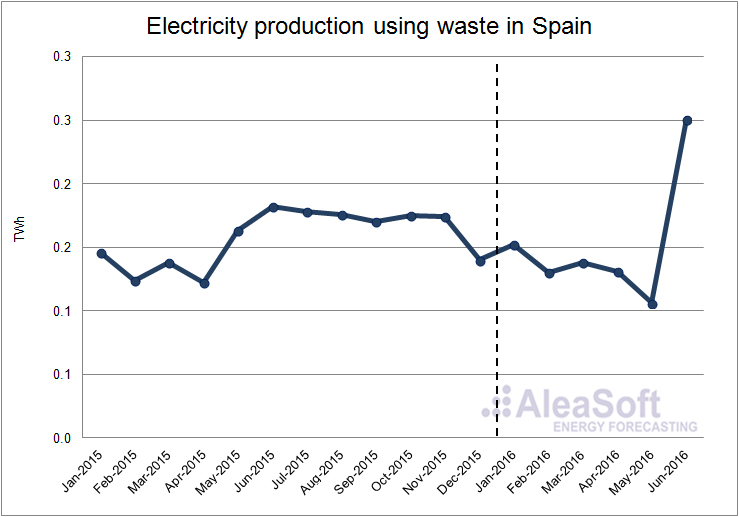
Evolution of electricity production using waste in Spain.
Data Source : REE.
It is important to notice that, since 2016 was a leap year, the first half of 2016 had an extra day compared to the first half of 2015. This affects the value of the growth of the gross demand and productions, which, due to purely calendar effects, already includes an increase of approximately 0.6% in the whole half of the year.
Prices of fuels for electricity generation
In the first half of 2016 the prices of the main fuels used in electricity generation were lower than in the first half of 2015. Although since February 2016 the prices slowed the downward trend and the Brent barrel price began to recover, they did not reach the level of the first half of 2015.
The average price of the Zeebrugge gas during the first half of the year was 13.05 €/MWh, 8.20 €/MWh lower than the first half of 2015.
The average price of the barrel of Brent oil during the first half of 2016 was $39.70, $18.17 less than the first half of the previous year.
The price of CIF ARA European coal decreased by 12.83 $/t in interannual terms in the first half of 2016, settling at 46.93 $/t.
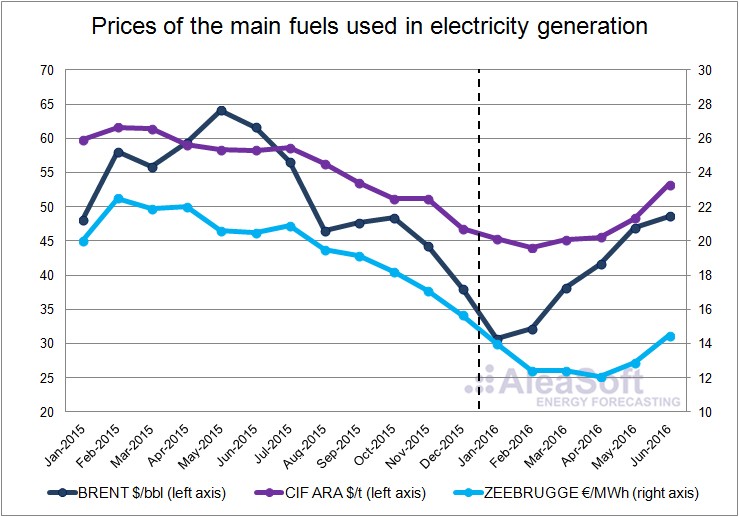
Evolution of the price of the main fuels used in electricity generation.
Data source: BRENT – EIA, CIF ARA – EEX, ZEEBRUGGE- NetConnect Germany.
Price of CO2 emission rights
The price of the CO2 emission rights in the first half of 2016 was 5.68 €/t on average, 1.52 €/t less that the same half of 2015. During the second quarter of this year, the price started recovering but this behavior stopped by the end of June at the time of the Brexit decision, as UK is one of the most important member countries supporting the EU Emissions Trading System.
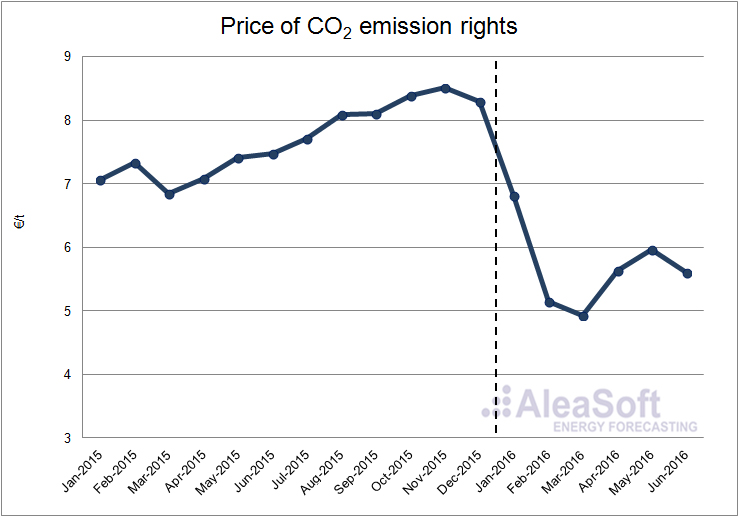
Evolution of the price of CO2 emission rights.
Data source: EEX.
Spain-Portugal Interconnection
In the first half of the year, the balance of the electricity exchanges between Spain and Portugal established Spain as a net importer, with 4044 GWh, making a difference with the first half and the whole year 2015 when Spain exported more electricity than it imported.
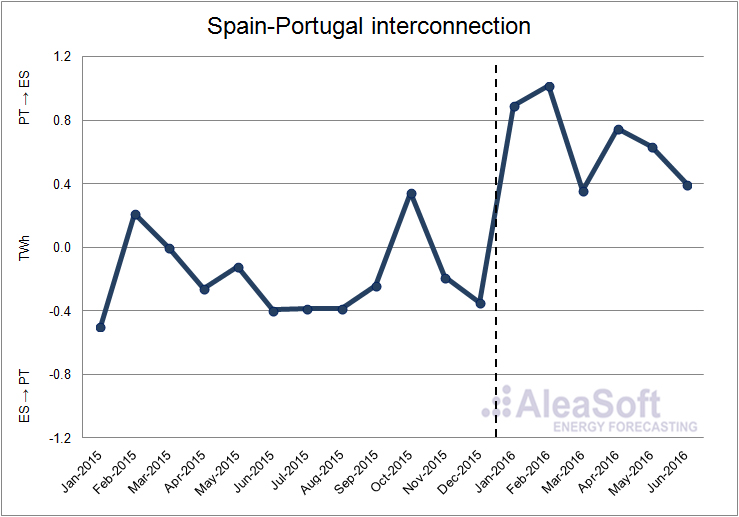
Evolution of the monthly net balance of the interconnection between Spain and Portugal. Positive values indicate that Spain imports electricity from Portugal, while negative values indicate that Spain exports electricity to Portugal.
Data sources: ENTSO-E and REE.
Spain-France Interconnection
The balance of the electricity exchanges between Spain and France during the first half of 2016 established Spain as a net importer, the same situation that occurred considering both the first half and the whole year 2015. The net balance of the first half of 2016 was that Spain imported 2490 GWh from France.
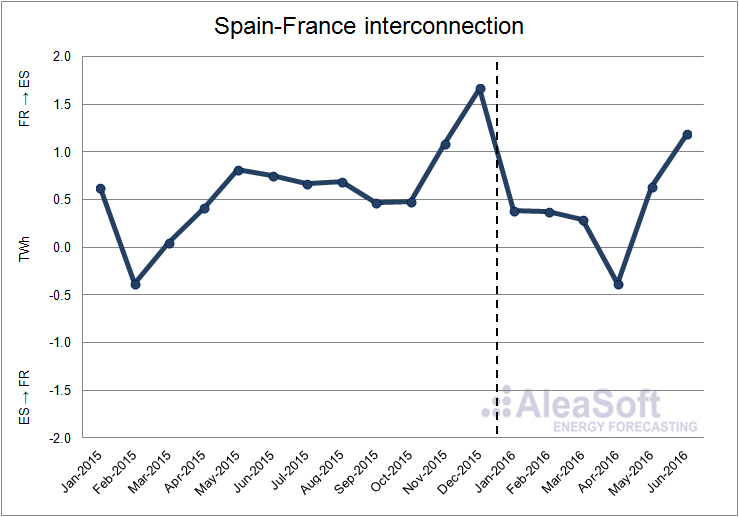
Evolution of the monthly net balance of the interconnection between Spain and France. Positive values indicate that Spain imports electricity from France, while negative values indicate that Spain exports electricity to France.
Data sources: ENTSO-E and REE.
Price of the Spanish day-ahead Market
The average price of the day ahead market OMIE in Spain in the first half of 2016 was 30.11 €/MWh, 17.01 €/MWh lower than the same period of the previous year. There was a year-on-year decrease of the price in every month, the largest being in April where the average price, 24.11 €/MWh, was 21.23 €/MWh lower than the previous April. The main reason of the price fall was the increase of the hydroelectric, wind power and nuclear production. The minimum price of the first six month of the year was 2.30 €/MWh and the maximum, 66.71 €/MWh that occurred between 19 p.m. and 20 p.m. in March 19th.
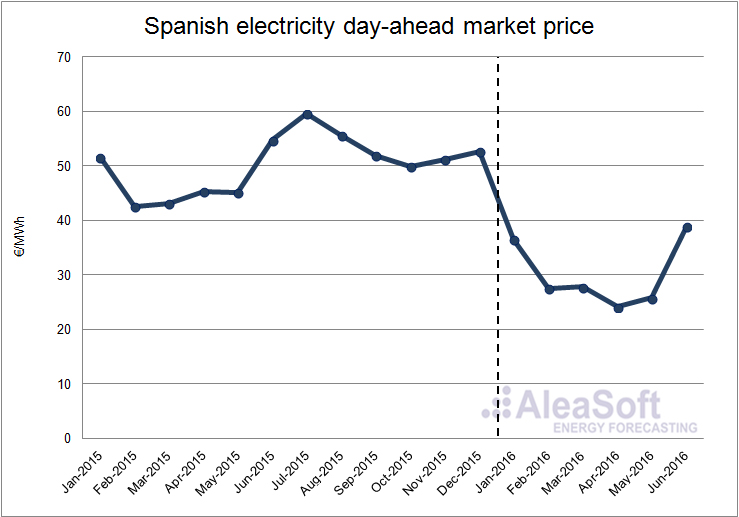
Evolution of Price of the Spanish electricity day-ahead Market.
Data sources: OMIE.
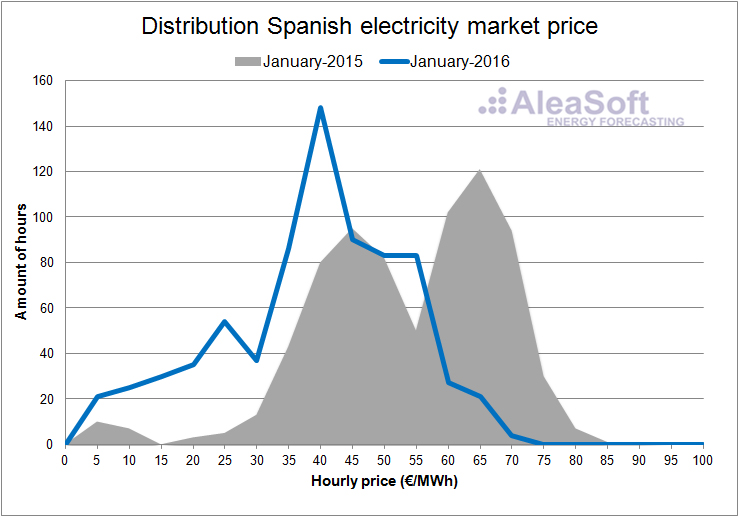
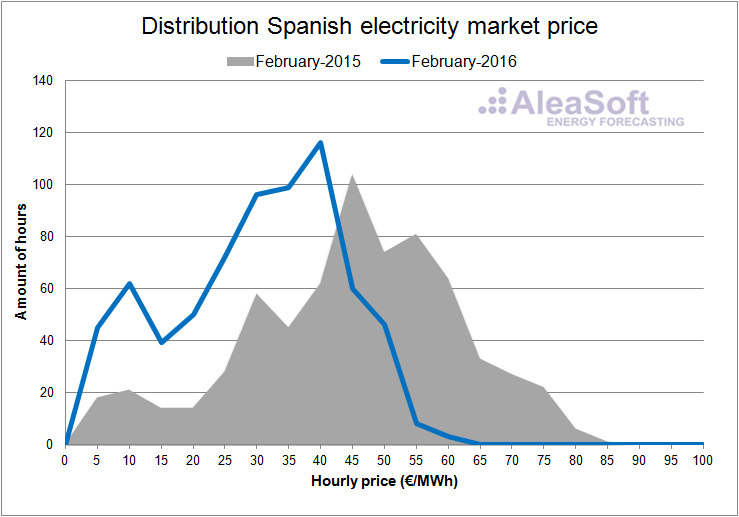
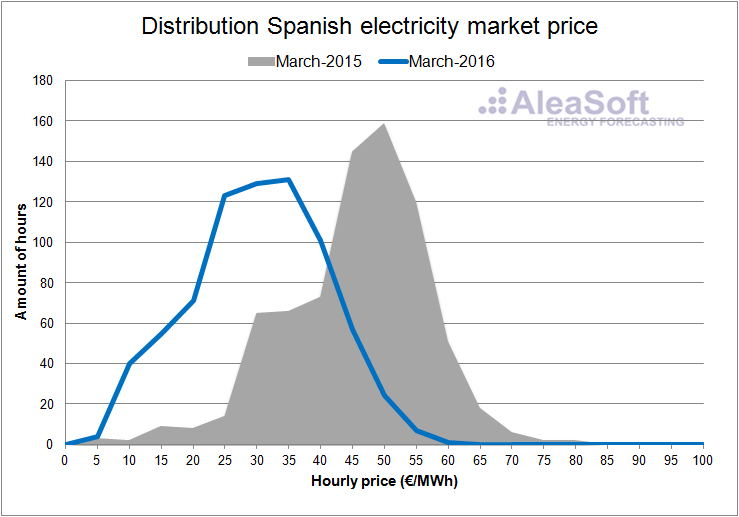
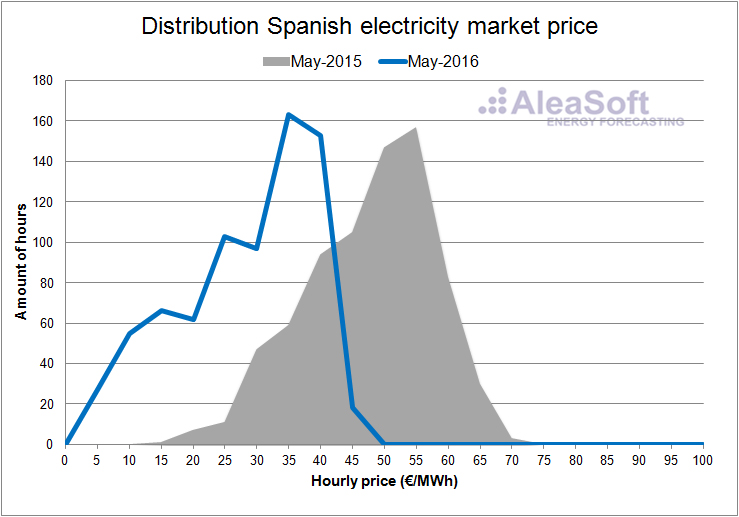
In the hourly price distribution plots of the day ahead market in Spain for each month of the first half of the year, one can clearly see how the prices in 2016 are shifted toward lower values with respect to the same months of 2015.
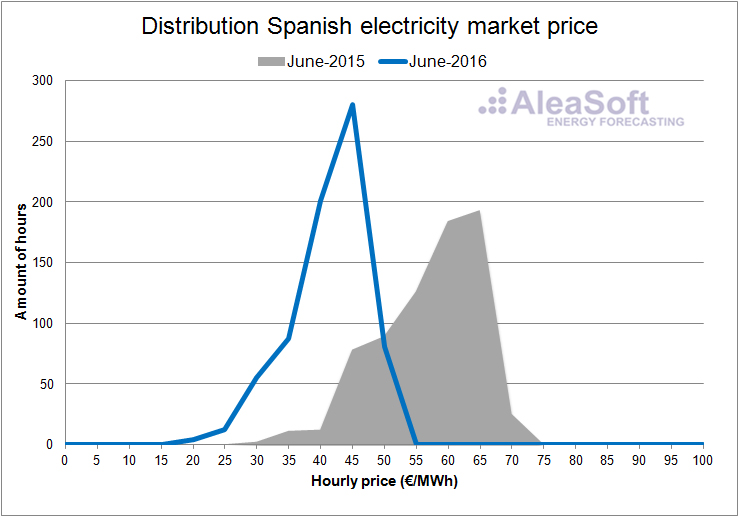
Distribution of the hourly price of the Spanish day-ahead market.
Data source: OMIE.
Concerning the correlation between the prices in the day ahead markets in Spain and Portugal, the fraction of hours where the price in Portugal was lower than the price in Spain greatly increased in the first half of 2016. At the same time, the fraction of hours with market coupling decreased.
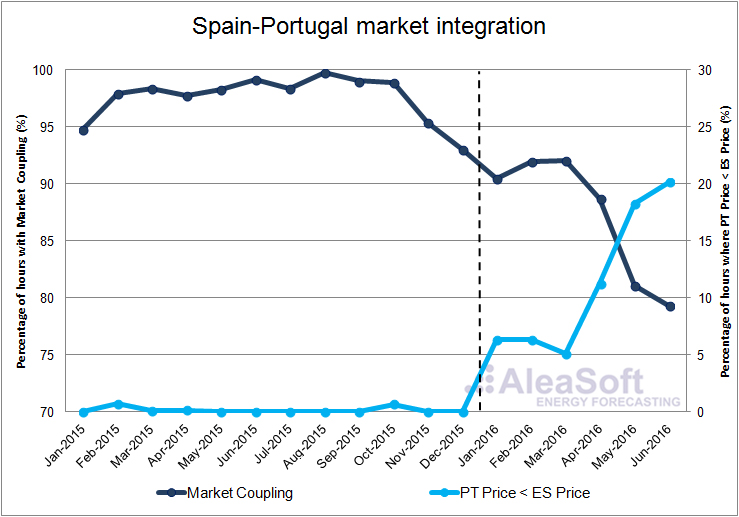
Evolution of the monthly fraction of hours with market coupling and the fraction of hours where the price in Portugal was lower than the price in Spain.
Data source: Prepared by AleaSoft from data published by OMIE.