AleaSoft Energy Forecasting, November 14, 2025. One of the most significant transformations in the electricity sector in recent decades has been the emergence of renewable energy. These clean sources have reshaped the way electricity is generated, modifying the energy mix and forcing both the market and the electricity grid to adapt.
First stage: public support and incentives
During the 2000s, many European countries, including Spain and Germany, began to promote the installation of renewable energy such as wind and solar energy. The aim was to reduce CO₂ emissions, decrease dependence on imported fossil fuels and meet international environmental commitments.
To make these technologies viable, which at the time were costly, governments established support schemes such as production premiums that added an incentive to the market price, regulated tariffs (feed‑in tariffs) that guaranteed a fixed price per MWh for several years, investment subsidies to support the creation and development of new plants and renewable energy capacity auctions.
Wind energy: the first to take off
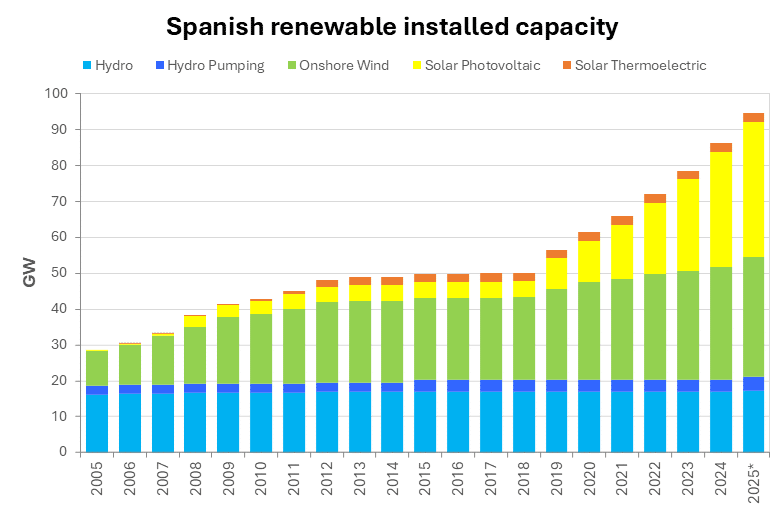
Wind energy was the first renewable source to achieve significant large‑scale development. Thanks to its technological maturity, lower cost compared with other renewable technologies and the high availability of resources in certain regions, thousands of wind turbines were installed across Europe.
Spain became one of the world leaders in installed wind capacity, alongside Germany, Denmark and the United States. Large plains, mountainous areas and coastal sites offered ideal conditions for this clean energy source.
The solar photovoltaic energy revolution
Solar photovoltaic energy began as a more expensive technology, but its evolution has been remarkable. Thanks to increased global production, especially in China, and improved panel efficiency, its cost has fallen by more than 80% since 2010.
This has enabled massive deployment, both through large‑scale solar plants and small‑scale rooftop self‑consumption systems. Today it is one of the most competitive technologies in the market.
New models: self‑consumption and energy communities
Falling costs and regulatory advances have opened the door to new energy models. Self‑consumption allows households and businesses to produce their own electricity through solar panels. In addition, with shared self‑consumption, several homes or businesses can benefit from the same installation.
Energy communities have also emerged, enabling groups of citizens to participate collectively in the generation, storage and management of renewable energy. This democratises access to clean energy and strengthens the local social and economic fabric.
Integration into the electricity market
Initially, renewable technologies did not participate directly in the electricity market, as they had guaranteed fixed tariffs. However, over time and with cost reductions, new installations have begun competing in the market on an equal footing with other technologies.
Furthermore, many projects are financed through Power Purchase Agreements (PPA), long‑term contracts that provide stability to producers and investors. Renewable energy is no longer an exception; it is now the cornerstone of the current and future electricity system.
Technical and management challenges
Although it is a goal of the international community, the growth of renewable energy brings important challenges. In electricity generation, these sources are variable and intermittent, as the availability of solar or wind energy cannot be controlled. For this reason, the greater the renewable energy generation, the more necessary energy storage, such as batteries or pumped hydro, becomes in order to reuse surplus energy generated during production peaks at times of lower generation.
In addition, as self‑consumers and energy communities become active participants in the electricity market, reinforcement of the electricity grids is necessary to integrate a wider distribution of generation, along with the digitalisation of the system to implement more accurate and advanced demand management. Overcoming these challenges is key to achieving a 100% renewable, reliable and secure system.
This publication is the third instalment in a series on the main milestones of the electricity system and its outlook for the coming years, entitled “The electricity system in evolution”. The objective is to provide an updated and structured overview of the present and future of the European electricity system.
Forecasts and analysis of AleaSoft Energy Forecasting for renewable energy and storage projects
AleaSoft Energy Forecasting, through its AleaGreen division, provides long‑term forecasts, essential for the financing of renewable energy projects, the signing of PPA contracts, asset valuation and the design of hedging strategies. The services offered by AleaGreen include production forecasts for different types of renewable energy plants, accompanied by the corresponding price forecasts, as well as forecasts of guarantees of origin.
In addition, the AleaStorage division analyses the viability of battery storage projects, both stand‑alone and hybridised with renewable energy plants, estimating their long‑term revenues and profitability, optimising their operation and providing tailored analyses for different business models.
Source: AleaSoft Energy Forecasting.