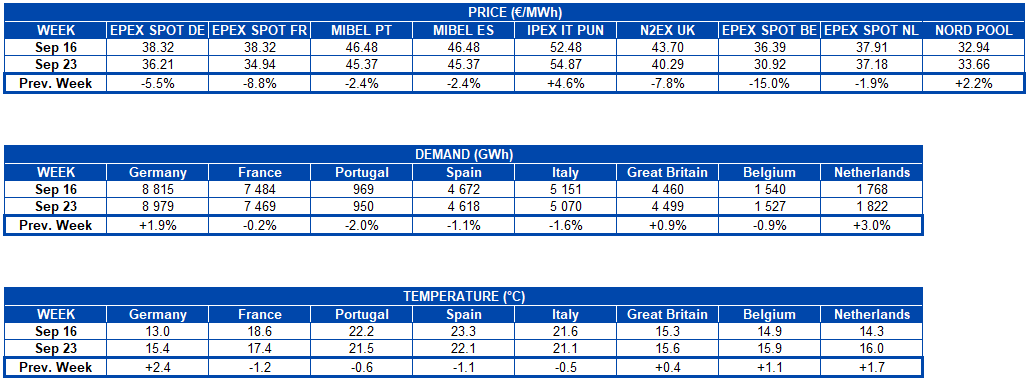
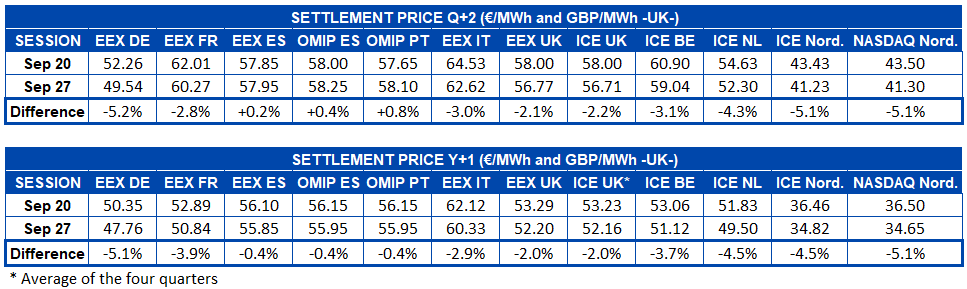
AleaSoft, September 30, 2019. In AleaSoft the analysis of the main European electricity markets was carried out in the week of September 23, in which the prices of most of the markets fell compared to the previous week. The main cause of this decline was the increase in the renewable energy production, mainly wind energy production, which grew in all the countries analysed. The decline in the fuel and CO2 prices also favoured the falls in the electricity markets.
Brent, fuels and CO2
In the week of September 23, the prices of Brent oil futures for the month of November in the ICE market experienced, in general, a downward trend, with the exception of Thursday, September 26, when there was a rise of 0.6% with respect to the settling price of the previous day. Despite the slight rise of the previous day, the behaviour presented throughout the week led to a settling price of $61.91/bbl on Friday, September 27, a value 3.7% lower than that corresponding to the same day of the previous week. This behaviour is influenced by the recovery in production levels in Saudi Arabia, as well as by the uncertainty about global economic growth and the trade dispute between China and the United States.
The prices of TTF gas futures in the ICE market for the month of October, the last days of last week remained stable ranging between €11.95/MWh and €12.04/MWh. This price stabilization was achieved after the declines in previous days. Therefore, the settling price reached on Friday, September 27, €11.94/MWh, was 6.1% lower than that corresponding to Friday of the previous week. The interruption in the fall in prices is related to the increase in demand associated with the decrease in temperatures and the forecast of lower wind energy production for this week.

With regard to the prices of API 2 coal futures in the ICE market for the month of October, the downward trend of the beginning of last week continued until Wednesday, September 25, when the minimum value of the week, $58.15/t, was reached, a settling price 6.4% lower than that of Wednesday, September 18. Subsequently, the prices began to recover slowly, closing on Friday, September 27 with a value of $59.65/t. This price is still $3.25/t below that reached on Friday of the previous week.
The prices of the CO2 emission rights futures in the EEX market for the December 2019 reference contract decreased practically throughout the past week, except for Thursday, September 26. This day the prices rose 1.7% over the previous day reaching a value of €25.64/t. At the end of the week, on Friday the price fell again, remaining at a value of €25.30/t, which represents €0.15/t below the minimum value reached the previous week, corresponding to September 18.
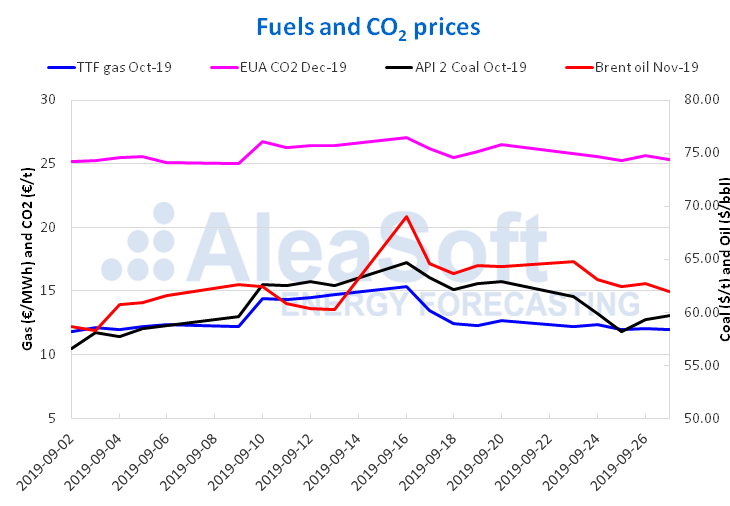
Sources: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ICE and EEX.
European electricity markets
The prices of most European electricity markets decreased last week compared to the week of September 16. This decline did not occur in the IPEX market in Italy and the Nord Pool market in the Nordic countries. The most noticeable inter-weekly change was seen in the EPEX SPOT market in Belgium, which had an average price last week of €30.92/MWh, representing a 15% drop from the average price of the week of September 16. In general, the markets experienced declines of between 1.9% and 15% already commented. The Italian and Nordic markets presented increases of 4.6% and 2.2%, respectively.
This drop in prices in most markets has among its main causes the increased production with renewable energy sources. Fundamentally, the wind energy production was quite favoured compared to the previous week in all the markets analysed. It also adds to the causes, the decreasing trend that fuel prices showed during the past week.
When analysing the figures for electricity demand in the week just concluded, no major changes are observed. The differences in one direction and another, in the set of countries analysed in AleaSoft practically cancel out. In fact, the difference in the global demand of all these countries shows an increase of just 0.2% compared to the week of September 16. Individually, the differences in electricity demand in the countries analysed range between ‑2.0% and 3.0%. For its part, the temperature rose in the coldest countries, with increases between 0.4°C and 2.4°C compared to the previous week. Meanwhile, in France, Portugal, Spain and Italy there were slight decreases in temperature, the most notable being in Spain and France, ‑1.1°C and ‑1.2°C, respectively.
As relevant data, in the sessions of Saturday 28 and Sunday 29, the EPEX SPOT markets in Belgium and Germany reached negative prices for some hours in the early morning valley. This phenomenon usually occurs when, as happened this weekend, high renewable energy production is combined with low electricity demand.
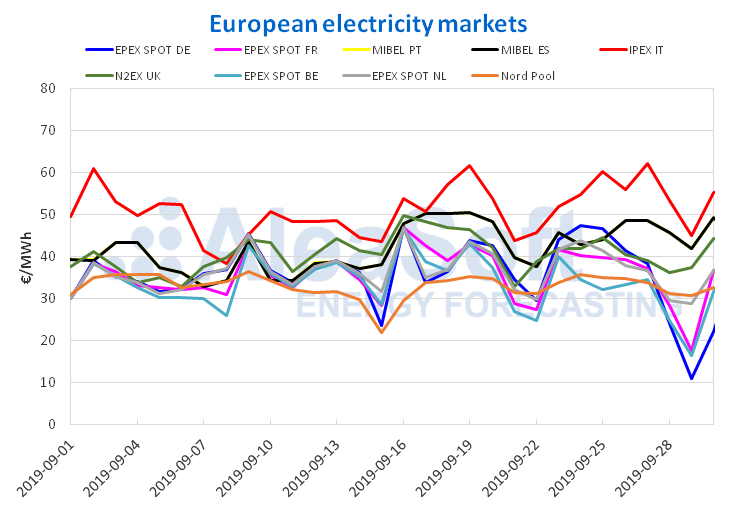
Sources: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from OMIE, EPEX SPOT, N2EX, IPEX and Nord Pool.
Electricity futures
The prices of European electricity futures for the first quarter of 2020 ended last week with lower values than those of the previous week in most markets. The main declines were recorded in the EEX markets in Germany and those of ICE and NASDAQ in the Nordic countries. The only markets where prices rose were EEX in Spain and OMIP in Spain and Portugal, which quoted a little higher at the end of last week.
Similarly, European electricity futures for the year 2020 on Friday 27 were down compared to the previous Friday. In this case, the futures of Germany in the EEX market and those of the Nordic countries in the NASDAQ market were also those that presented the greatest variation with a difference of ‑5.1%. The ICE markets in the Nordic countries, Belgium and the Netherlands, as well as the EEX market in France, also stand out in this fall. At the other extreme, the EEX market in Spain and OMIP market in Spain and Portugal remained with little variation and closed last Friday with a difference of ‑0.4%.
Wind and solar energy production
Last week there was a growth of wind energy production in much of the European continent. Among the most significant week‑to‑week increases was that of Italy, with 50%. In France, the growing trend that began in the week of September 9 remained, and this time increased by 37%. The production recorded in Germany increased by 32% compared to the previous week and in Portugal by 21%. Since the end of August, in Spain there have been increases in generation with this technology, but last week it was the lowest compared to the rest of the countries analysed, being 12%. During this week, the wind energy production is expected to continue in this way in Germany, Spain and Italy, and declines are expected in France and Portugal.
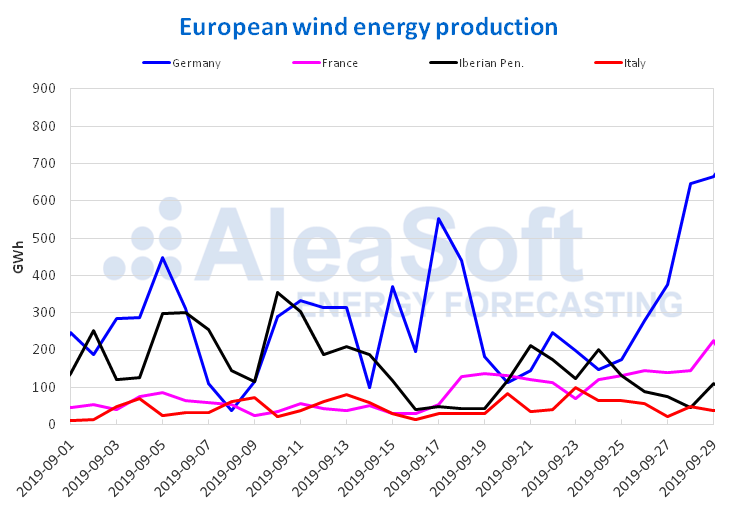
Sources: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
In the whole of photovoltaic and solar thermal energy production, the solar energy production had different behaviours last week in the three countries analysed. In the case of Spain, there was a large increase of 59%. The values for Italy were similar to those of the previous week, ending last week with 0.2% growth. In Germany, the solar energy production suffered a ‑45% drop. For this week, AleaSoft expects recoveries in Germany and Italy, and similar values or even lower in the case of Spain.

Sources: Prepared by AleaSoft using data from ENTSO-E, REE and TERNA.
Source: AleaSoft Energy Forecasting.